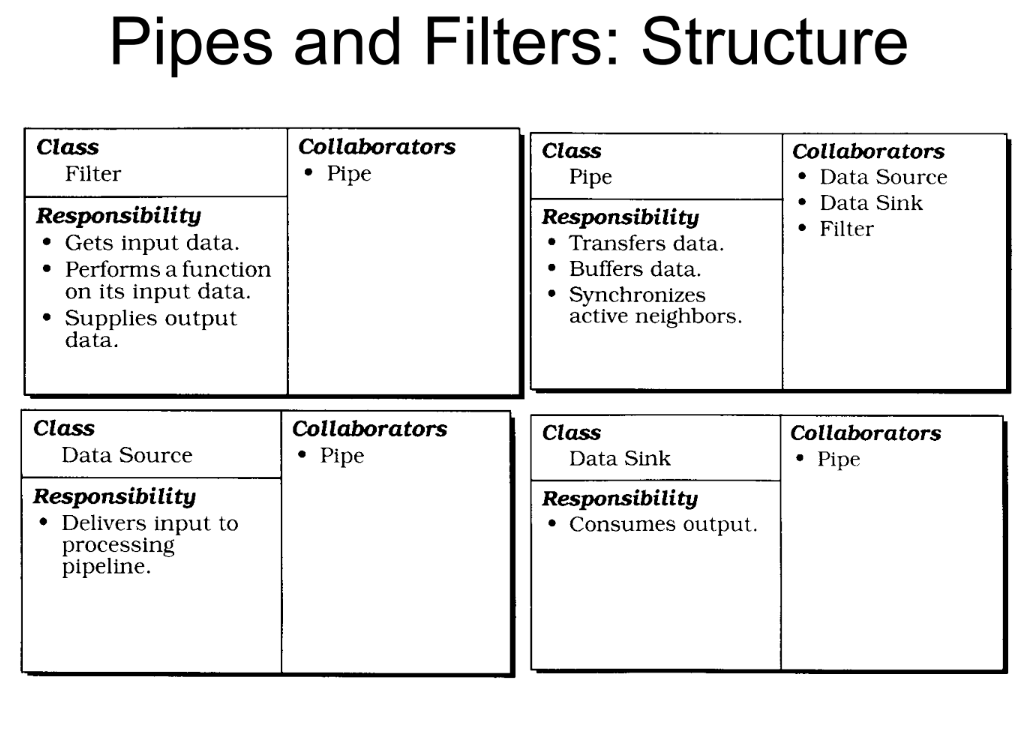
Pipes and Filters is a pattern where data is processed through a series of components (filters) connected by pipelines (pipes). Each filter performs a specific task on the input data, and the output of one filter becomes the input for the next.
- For processing data streams
- Data flows through pipes between adjacent filters
- You can have push(write), pull (read) or push-pull pipelines
Usage
- UNIX - Many utilities work as filters on text streams.
- CMS Pipelines - Filter components for IBM mainframe systems.
- LASSPTools - Filters for numerical analysis and visualisation.
- Web apps - Servlets filter and process HTTP requests/responses.
Benefits
- Recombination - Filters can be rearranged flexibly.
- Parallelism - Filters can execute concurrently.
- Reuse - Filters can be reused in other pipelines.
- Prototyping - Pipelines are easy to prototype.
Drawbacks
- Performance - Data copying between filters, context switching.
- Difficulty with shared state - Expensive to share state between filters.
- Error handling - Hard to implement transactions across filters.
Example
Imagine a photo editing application where filters like brightness adjustment, color correction, and cropping are applied to an image. Each filter is a component, and they are connected in a sequence (pipe) to modify the image.