MVC is a software architectural pattern used for designing user interfaces. It divides an application into three interconnected components: Model, View, and Controller.
- Parts,
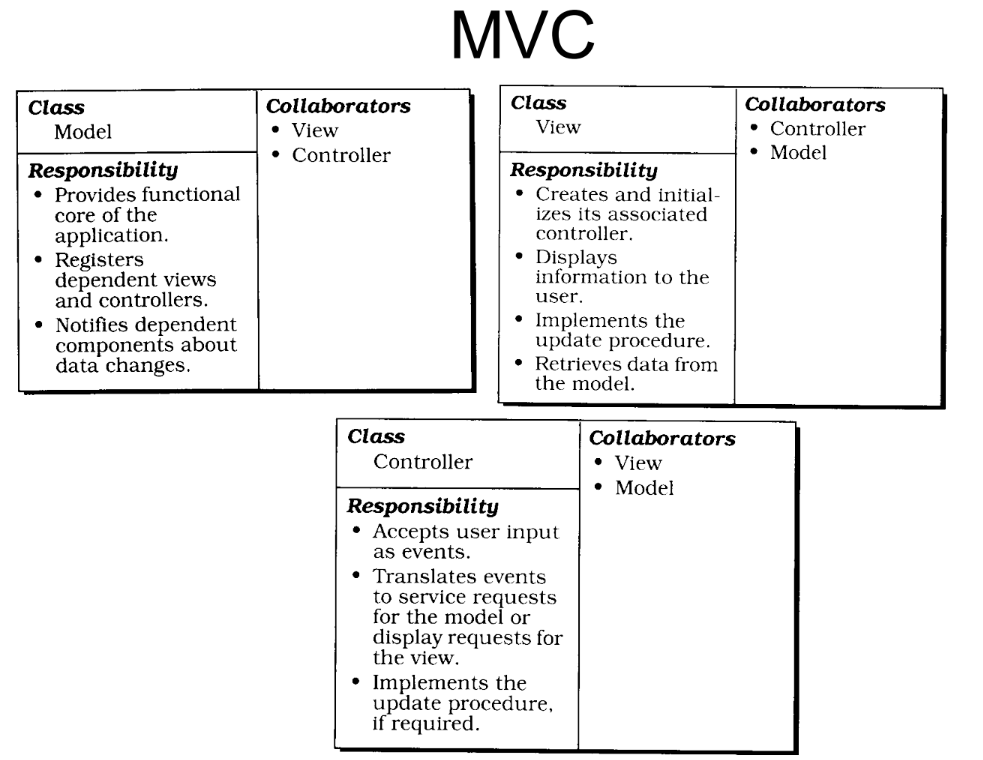
- Model -> Data and data logic
- View -> Display information to the user
- Controller -> Handles request flow
Usage
- Smalltalk - Originated the MVC pattern.
- MFC, Java Swing - GUI frameworks based on MVC.
Benefits
- Multiple views - Different visualizations of same data.
- Pluggable views/controllers - New ones can be added flexibly.
- Separated concerns - Model, view and control logic are isolated.
Drawbacks
- Complexity - Many moving parts to coordinate.
- Excessive updates - Too many cascading model updates.
- Close coupling - Views/controllers often too dependent on model.
Example
In a web application, the Model represents the data fetched from a database, the View displays the user interface, and the Controller manages the interactions between the Model and the View.