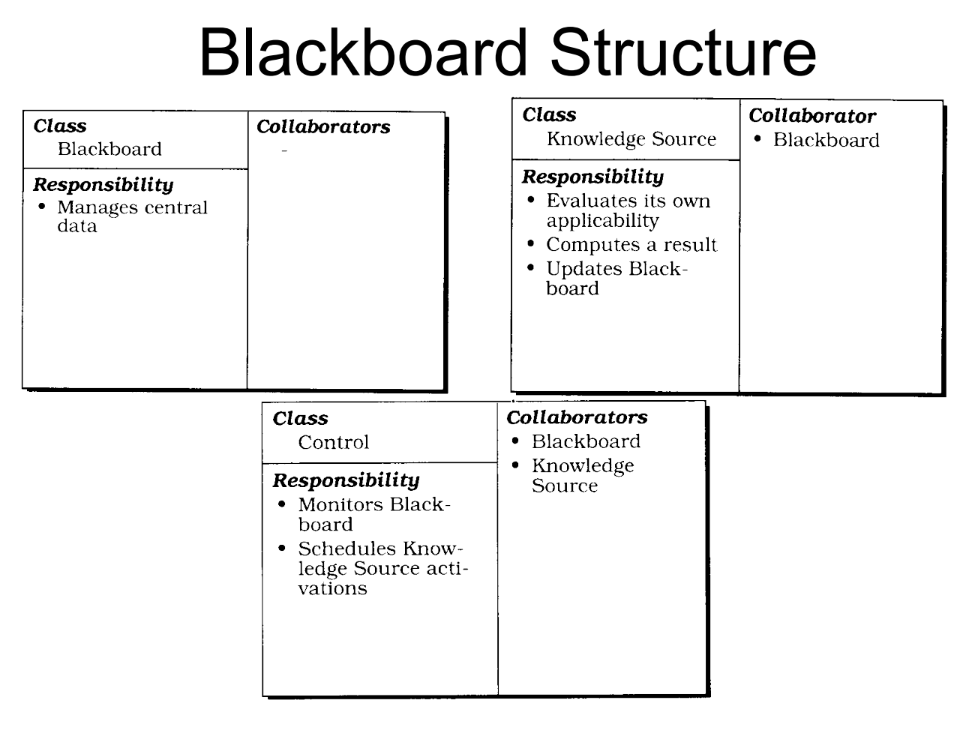
The Blackboard pattern involves multiple independent components working on a shared data structure called the “blackboard.” These components contribute their expertise by modifying and examining the blackboard data until a solution is reached.
- Useful when no clear deterministic solution exists.
- Specialised subsystems assemble knowledge to incrementally build a partial or approximate solution
- Parts: Blackboard, Knowledge source, control
Variants
- Production System
- Blackboard -> Working memory
- Knowledge Source -> Condition-action rules
- Control -> conflict resolution module
- Repository
- Blackboard -> Data
- Knowledge source -> Application
- Control -> User input
Usage
- HEARSAY-II - Speech recognition system.
- HASP/SIAP - Submarine detection system.
- Crysalis - Determine protein molecule structure.
Benefits
- Experimentation - Alternate algorithms and heuristics can be tried.
- Incremental solution - Partial solutions built up over time.
- Fault tolerance - Can cope with noisy or incomplete data.
Drawbacks
- Inefficiency - Wasteful hypothesis testing.
- No guarantee of correct solution - Depends on knowledge sources.
- Control strategy - Hard to define optimal control heuristics.
- Complex testing - Non-deterministic behavior.
Example
In artificial intelligence or complex problem-solving systems, different algorithms or modules work together by updating and analyzing a shared repository of information (the blackboard) to solve a problem collaboratively.